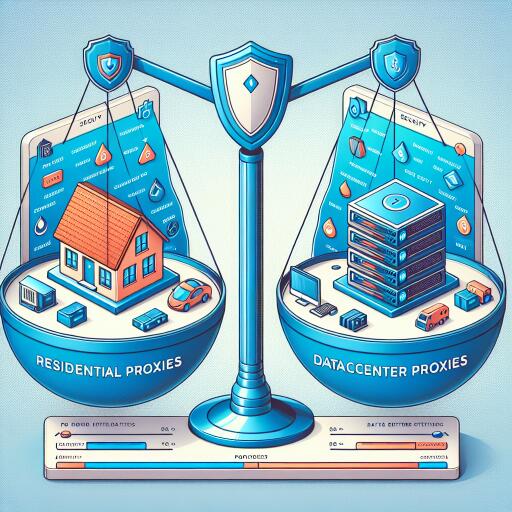
Residential Proxies vs. Datacenter Proxies: Navigating the Best Choice
In today’s digital age, your online presence and activities are constantly being monitored, whether for marketing purposes, cybersecurity, or even more intrusive surveillance. To navigate this landscape while maintaining anonymity and securing online activities, the use of proxies has become increasingly popular. Among the plethora of options available, residential and datacenter proxies stand out. Understanding the differences between these two can help in choosing the right option for your needs.
What are Residential Proxies?
Residential proxies route your internet traffic through an intermediary server that carries an IP address tied to a physical location. This IP address is assigned by an Internet Service Provider (ISP) to a homeowner, making it seem as though digital requests originate from a regular internet user. This aspect offers high anonymity and is less likely to be flagged or blocked on most platforms.
What are Datacenter Proxies?
Conversely, datacenter proxies are not affiliated with ISPs and do not correspond to a specific residential address. They are provided by third-party companies from data centers, branding them with a completely separate IP pool. This detachment offers faster speeds and a lower cost, albeit at a higher risk of detection and potential blacklisting by some websites sensitive to proxy use.
Key Differences and Considerations
When deciding between residential and datacenter proxies, several factors come into play, including:
- Anonymity: Residential proxies offer a higher level of anonymity since they are indistinguishable from regular internet users. In contrast, the shared nature of many datacenter proxies can sometimes flag them as suspicious to websites.
- Price: Datacenter proxies are generally cheaper and more accessible than residential proxies because they are easier to maintain and come from a pooled resource. Residential proxies require ISPs to allocate genuine IP addresses, driving up costs.
- Speed and Performance: Datacenter proxies usually provide higher speeds due to the powerful hardware in data centers. Although residential proxies are improving, their speed can still be contingent upon the homeowner’s internet connection.
- Website Accessibility: Some platforms have stringent measures against proxies and can easily detect and block datacenter IP addresses. Residential proxies are less prone to this because they mirror legitimate user behavior more closely.
Choosing the Right Option
The decision between residential and datacenter proxies depends on your specific requirements:
- For tasks requiring high anonymity and fewer chances of being blocked, residential proxies are preferable.
- On the flip side, if speed and cost-effectiveness are your priorities, and the risk of detection is minimal or manageable, datacenter proxies might be the better choice.
Ultimately, the right proxy service hinges on a balance between anonymity, cost, speed, and the nature of your online activities. It’s advisable to carefully assess your needs or consult with a specialist to identify the most suitable type of proxy for your scenario.
Conclusion
In the vast and sometimes murky waters of the internet, maintaining privacy and security is paramount. Through the strategic use of residential or datacenter proxies, individuals and organizations can navigate online spaces more safely and efficiently. Whether you opt for the authenticity of residential proxies or the speed and economy of datacenter proxies, understanding their differences is the first step towards smarter, safer internet usage.